This article guides you through installing PHP 8.4 on Debian 12, setting up PHP-FPM for efficient request handling, and integrating it with the Apache web server.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, you need to:
- Have access to a Debian 12 instance as a non-root sudo user.
Add the PHP PPA Repository
Debian 12's default APT repositories may not include the latest PHP releases. The SURY repository, maintained by Debian PHP package maintainer Ondřej Surý, provides up-to-date PHP versions and is widely trusted in the community.
-
Update the system package index and upgrade existing packages.
console
$ sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y
Install required dependencies.
$ sudo apt install -y lsb-release apt-transport-https ca-certificates
Import the SURY GPG key to verify the repository's package authenticity.
$ sudo wget -O /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/php.gpg https://packages.sury.org/php/apt.gpg
Add the SURY PHP repository to your system's APT sources.
$ echo "deb https://packages.sury.org/php/ $(lsb_release -sc) main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/php.list
Update the APT package index again to include the new repository.
$ sudo apt update -y
PHP 8.4 is currently available through the packages.sury.org/php repository. You can verify the available version in your APT sources by running:
$ sudo apt policy php
-
Output.
php: Installed: (none) Candidate: 2:8.4+96+0~20250402.56+debian12~1.gbp84a5b7 Version table: 2:8.4+96+0~20250402.56+debian12~1.gbp84a5b7 500 500 https://packages.sury.org/php bookworm/main amd64 Packages 2:8.2+93 500 500 https://deb.debian.org/debian bookworm/main amd64 Packages 500 https://debian.mirror.constant.com bookworm/main amd64 PackagesThis confirms that PHP 8.4 is available from the SURY repository.
You can also visit the PHP Releases page to verify the latest official version.
Install PHP 8
With the SURY repository enabled, you can now install PHP 8.4 and configure commonly used extensions. These are required for features like database access, string manipulation, file handling, and API communication.
-
Install PHP 8.4.
$ sudo apt install -y php8.4
Verify the installed version.
$ php8.4 -v
-
Output:
PHP 8.4.6 (cli) (built: Apr 11 2025 02:09:29) (NTS) Copyright (c) The PHP Group Zend Engine v4.4.6, Copyright (c) Zend Technologies with Zend OPcache v8.4.6, Copyright (c), by Zend Technologies -
List installed PHP versions and optionally set PHP 8.4 as the default system version.
$ ls /etc/php
If only PHP 8.4 is installed, you can set it as the default system-wide PHP interpreter using update-alternatives.
$ sudo update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/php php /usr/bin/php8.4 84
Then verify:
$ php -v
Install common PHP extensions used for database, networking, and string handling.
$ sudo apt install -y php8.4-mysql php8.4-curl php8.4-xml php8.4-mbstring
-
php8.4-mysql: MySQL/MariaDB database supportphp8.4-curl: Enables cURL for remote data fetchingphp8.4-xml: Handles XML parsingphp8.4-mbstring: Supports multibyte string encoding (important for UTF-8)
-
List the active PHP modules to verify installation.
$ php8.4 -m
-
This lists all active PHP modules, including the extensions you just installed.
Install PHP 8 FPM
PHP-FPM (FastCGI Process Manager) separates PHP execution from the web server, improving performance and scalability. In this section, you’ll install PHP-FPM 8.4, configure its socket permissions, and ensure it starts on boot.
-
Install PHP 8.4 FPM.
$ sudo apt install -y php8.4-fpm
Open the default PHP-FPM pool configuration file.
$ sudo nano /etc/php/8.4/fpm/pool.d/www.conf
Define the Unix socket PHP-FPM will listen on.
listen = /run/php/php8.4-fpm.sock
Set socket permissions for Apache access.
listen.owner = www-data
listen.group = www-data
listen.mode = 0660
-
These settings ensure Apache can communicate with PHP-FPM via the socket.
-
Enable PHP-FPM to start automatically on boot.
$ sudo systemctl enable php8.4-fpm
Restart the PHP-FPM service to apply the configuration changes.
$ sudo systemctl restart php8.4-fpm
Verify PHP-FPM is running.
$ sudo systemctl status php8.4-fpm
-
Output:
● php8.4-fpm.service - The PHP 8.4 FastCGI Process Manager Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/php8.4-fpm.service; enabled; preset: enabled) Active: active (running) since Wed 2025-04-16 07:09:39 UTC; 13s ago Docs: man:php-fpm8.4(8) Process: 13047 ExecStartPost=/usr/lib/php/php-fpm-socket-helper install /run/php/php-fpm.sock /etc/php/8.4/fpm/pool.d/www.conf 84 (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Main PID: 13044 (php-fpm8.4) ...
PHP includes a built-in development server for lightweight testing. This method is ideal for validating that PHP is working correctly before setting up Apache or Nginx.
-
Create a test directory and PHP file.
$ mkdir ~/phptest && cd ~/phptest
Start the PHP development server:
$ php8.4 -S 0.0.0.0:8000
-
Open
http://SERVER-IP:8000in your browser.
This method is helpful for quick testing, but it’s not recommended for production use.
PHP-FPM runs as a separate service that handles PHP execution more efficiently than traditional mod_php. It listens on a Unix socket and works alongside your web server. In this section, you’ll integrate Apache with PHP-FPM using proxy_fcgi, then deploy a test PHP script to confirm the setup.
-
Install Apache.
$ sudo apt install -y apache2
Enable the proxy_fcgi and setenvif modules in Apache to handle PHP via PHP-FPM.
$ sudo a2enmod proxy_fcgi setenvif
Enable the PHP-FPM configuration for Apache.
$ sudo a2enconf php8.4-fpm
Restart the Apache service to apply the changes.
$ sudo systemctl restart apache2
Create a sample PHP application file.
$ sudo nano /var/www/html/sample.php
Add the following content to the file:
<?php
phpinfo();
?>
Allow HTTP traffic through the firewall.
$ sudo ufw allow 80/tcp
Reload the firewall configuration.
$ sudo ufw reload
Open a browser and visit:
http://SERVER-IP/sample.phpReplace SERVER-IP with your server’s actual IP address. You should see the PHP information page confirming the active PHP version and configuration.
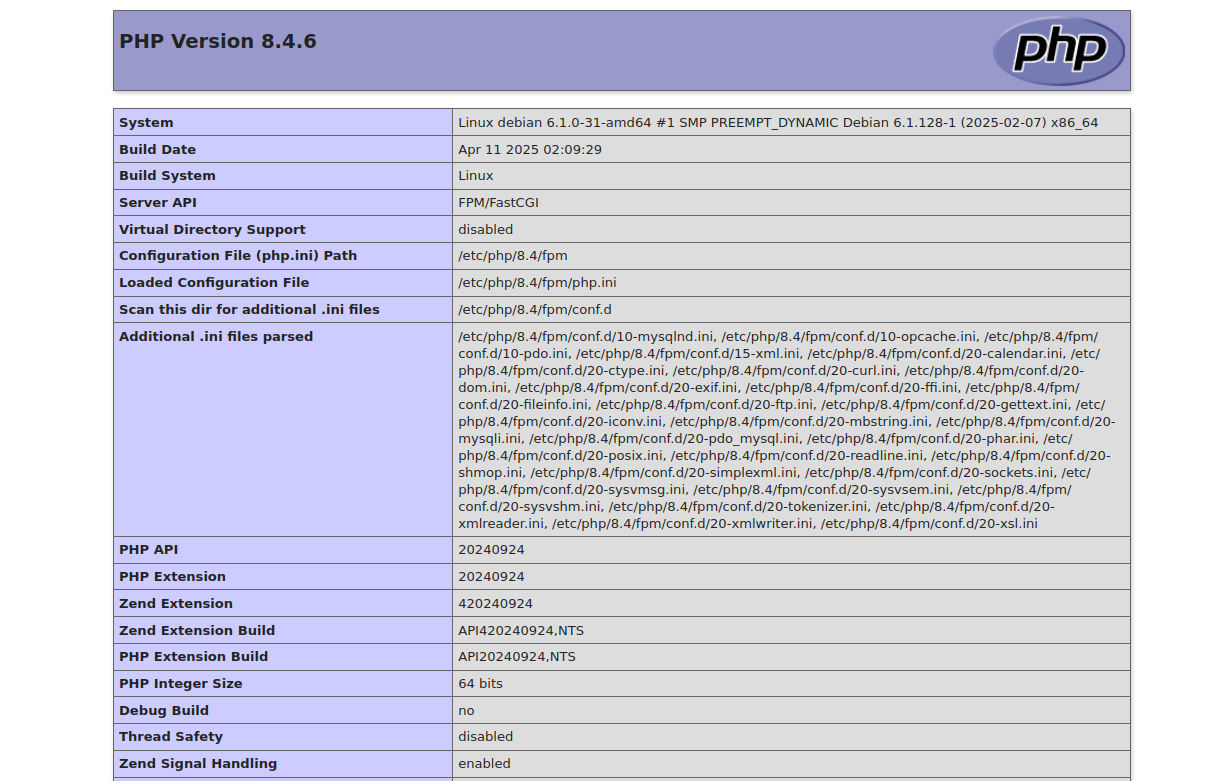
Conclusion
In this article, you installed PHP 8.4 and PHP-FPM on a Debian 12 server. You added the SURY repository to access the latest PHP packages, installed and verified PHP 8.4, configured PHP-FPM for efficient process management, and integrated it with the Apache web server. You also deployed a test PHP script to confirm the setup works as expected. With this environment in place, your server is now ready for hosting modern PHP applications.

